
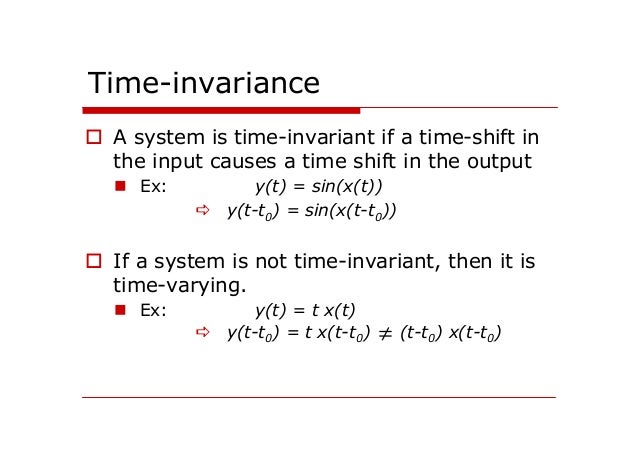
We state this fact as the following theorem. In mathematics and theoretical physics, an invariant differential operator is a kind of mathematical map from some objects to an object of similar type. This chapter presentsthe foundation of DSP: what it means for a system to be linear, various ways for breaking signalsinto simpler components, and how superposition provides a variety of signal processingtechniques.
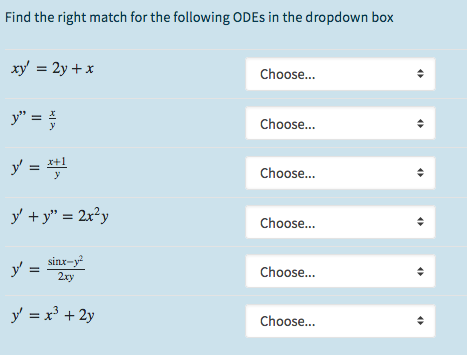
Linearizing the time-invariant form of Eq. We will see that solving the complementary equation is an important step in solving a nonhomogeneous differential equation. Key words and phrases: invariant dierent operators nonreductive homogeneous spaces space of horocycles isotropic pseudo-Riemannian spaces. The principal difficulty in studying delay differential equations lies in its. If we find two solutions, then any linear combination of these solutions is also a solution. General Solution to a Nonhomogeneous Linear Equation. An important difference between first-order and second-order equations is that, with second-order equations, we typically need to find two different solutions to the equation to find the general solution. Just as with first-order differential equations, a general solution (or family of solutions) gives the entire set of solutions to a differential equation. General form and an example have been covered in this. The Principle of Superposition is the sum of two or more solutions is also a solution.Since the wave equation is a linear homogeneous differential equation.
evolution equation which possess the superposition principle. Describing the general form of non homogeneous differential equation and solving it using the superposition method. In other words, we want to find a general solution. This leads to an integration of ordinary differential equations in a process of.

Īlthough simply finding any solution to a differential equation is important, mathematicians and engineers often want to go beyond finding one solution to a differential equation to finding all solutions to a differential equation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
